![[red stuffed lobster logo]](http://worker.jart.workers.dev/redbean/redbean168.png)
redbean makes it possible to share web applications that run offline as
a single-file αcτµαlly pδrταblε εxεcµταblε zip archive which
contains your assets. All you need to do is download
the redbean.com program below, change the filename to .zip,
add your content in a zip tool like InfoZIP, and change the extension
back to .com.
redbean can serve 1 million+ gzip encoded responses per second on a cheap personal computer. That performance is thanks to zip and gzip using the same compression format, which enables kernelspace copies. Another reason redbean goes fast is that it's a tiny static binary, which makes fork memory paging nearly free.
redbean is also easy to modify to suit your own needs. The program itself is written as a single .c file. It embeds the Lua programming language which lets you write dynamic pages.
this is an old version
click here for the latest redbean
redbean-0.3.1.com
460kb - PE+ELF+MachO+ZIP+SH
42013bdbd212ec43ffce9d086ecca0b3d6e464ab56628a984ad7e0fe6902bb1a
redbean-0.3.1.com.dbg
4m - ELF debugger data (optional)
59d59140bc51a1f6e7e6ace8beac63ece1058eeee98d52e90915a2e1f9b56506
redbean.c
source code
redbean-tiny-0.3.1.com (smaller but more cryptic errors)
372kb - PE+ELF+MachO+ZIP+SH
9a00227b3bdfdfc9f84aa4329075962717f6f75e0a2ab87ed44da2c574dcb251
redbean-tiny-0.3.1.com.dbg
3.7m - ELF debugger data (optional)
5d587f835e86603fbcc84bc546b0760b58f8d272e68d24623b1706381eee22a5
redbean-asan-0.3.1.com (huge but nearly memory safe)
1.8mb - PE+ELF+MachO+ZIP+SH
e49eb1f646492a534b3f93149d5bdf96f70a98f35b5cf0ed87f1b07d315632ab
redbean-asan-0.3.1.com.dbg
7.2m - ELF debugger data (optional)
1099aac5d9a22fe38917811e292a391fe8c89dad7b77559b6e8f498748dc6512
curl https://redbean.dev/redbean-0.3.1.com >redbean.com curl https://redbean.dev/redbean-0.3.1.com.dbg >redbean.com.dbg chmod +x redbean.com ./redbean.com -v bash -c './redbean.com -v' # zsh/fish workaround (we upstreamed patches!)
echo 'Write("<b>hello</b>")' >hello.lua
echo '<b>hello</b>' >hello.html
zip redbean.com hello.lua
zip redbean.com hello.html
./redbean.com -vv
curl -v http://127.0.0.1:8080/index.html
git clone https://github.com/jart/cosmopolitan && cd cosmopolitan make -j8 o//tool/net/redbean.com o//tool/net/redbean.com -vv
Assets can be listed by running the following command:
unzip -vl redbean.com # lists files
Which is also implemented as the default index page:
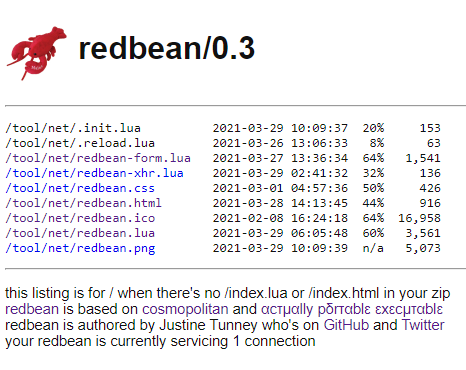
Assets can be added to the zip archive as follows:
zip redbean.com index.html # adds file zip -r redbean.com mirrored-website # adds directory
By default, anything you add to the archive gets compressed. Sometimes you don't want that to happen. A good example is video files. The web browser will want to send HTTP range requests to seek in the video, in which case redbean requires that the asset be uncompressed.
zip -0 redbean.com video.mp4 # adds file without compression
You can run redbean interactively in your terminal as follows:
redbean.com -vv CTRL-C # 1x: graceful shutdown CTRL-C # 2x: forceful shutdown
The index.lua and index.html names are special
since they're used to automatically figure out how to serve directories.
Such files can appear in any directory, however the root directory is
special. The default action for / is to show a listing page
showing the contents of your zip central directory.
| -h | help |
|---|---|
| -v | verbosity [repeatable] |
| -d | daemonize |
| -u | uniprocess |
| -m | log messages |
| -b | log message bodies |
| -k | encourage keep-alive |
| -z | print port [useful with -p0 for automation]
|
| -D DIR | serve assets from local filesystem directory [repeatable] |
| -c INT | cache seconds |
| -r /X=/Y | redirect /X to /Y [repeatable]
|
| -R /X=/Y | rewrite /X to /Y [repeatable]
|
| -l ADDR | listen ip [default 0.0.0.0] |
| -p PORT | listen port [default 8080] |
| -L PATH | log file location |
| -P PATH | pid file location |
| -U INT | daemon set user id |
| -G INT | daemon set group id |
| -B STR | changes brand |
Any files with the extension .lua will be dynamically
served by redbean. Here's the simplest possible example:
Write('<b>Hello World</b>')
The request handler above should perform at 700,000 responses per second, without any sort of caching. In practice though, it ends up being closer to 300,000 responses per second, since once your response reaches 100 bytes redbean will do things like apply gzip compression automatically.
Here's an example of a more typical workflow for Lua Server Pages using the redbean API:
SetStatus(200)
SetHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain; charset=utf-8')
Write('<p>Hello ')
Write(EscapeHtml(GetParam('name')))
We didn't need the first two lines in the previous example, because they're implied by redbean automatically if you don't set them. Responses are also buffered until the script finishes executing. That enables redbean to make HTTP as easy as possible. In the future, API capabilities will be expanded to make possible things like websockets.
redbean embeds the
Lua standard library.
You can use packages such as
io
to persist and share state across requests and connections. In the
future, SQLite might be embedded too.
Your Lua interpreter begins its life in the main process at startup in
the .init.lua, which is likely where
you'll want to perform all your expensive one-time operations like
importing modules. Then, as requests roll in, isolated processes are
cloned from the blueprint you created.
/index.lua or /index.html file defined.
ProgramFOO() functions below. The init module load happens after redbean's arguments and zip assets have been parsed, but before calling functions like socket() and fork(). Note that this path is a hidden file so that it can't be unintentionally run by the network client.
/ listing page icon, embedded as a base64 URI.
getopt() in the C code, which stops parsing at the first non-hyphenated arg. In some cases you can use the magic -- argument to delimit C from Lua arguments.
Log.
kLogDebug. See Log.
kLogVerbose. See Log.
kLogVerbose. See Log.
kLogWarn. See Log.
kLogError. See Log.
data: URIs that do things like embed a PNG file in a web page. See encodebase64.c.
#fragment. The allowed characters are -/?.~_@:!$&'()*+,;=0-9A-Za-z and everything else gets %XX encoded. Please note that '& can still break HTML and that '() can still break CSS URLs. This function is charset agnostic and will not canonicalize overlong encodings. It is assumed that a UTF-8 string will be supplied. See escapeurlfragment.c.
&><"' which become &><"'. This function is charset agnostic and will not canonicalize overlong encodings. It is assumed that a UTF-8 string will be supplied. See escapehtml.c.
\uxxxx sequences for all non-ASCII sequences. HTML entities are also encoded, so the output doesn't need EscapeHtml. This function assumes UTF-8 input. Overlong encodings are canonicalized. Invalid input sequences are assumed to be ISO-8859-1. The output is UTF-16 since that's what JavaScript uses. For example, some individual codepoints such as emoji characters will encode as multiple \uxxxx sequences. Ints that are impossible to encode as UTF-16 are substituted with the \xFFFD replacement character. See escapejsstringliteral.c.
-.*_0-9A-Za-z and everything else gets %XX encoded. This function is charset agnostic and will not canonicalize overlong encodings. It is assumed that a UTF-8 string will be supplied. See escapeurlparam.c.
EscapeSegment except slash is allowed. The allowed characters are -.~_@:!$&'()*+,;=0-9A-Za-z/ and everything else gets %XX encoded. Please note that '& can still break HTML, so the output may need EscapeHtml too. Also note that '() can still break CSS URLs. This function is charset agnostic and will not canonicalize overlong encodings. It is assumed that a UTF-8 string will be supplied. See escapeurlpath.c.
EscapePath except slash isn't allowed. The allowed characters are -.~_@:!$&'()*+,;=0-9A-Za-z and everything else gets %XX encoded. Please note that '& can still break HTML, so the output may need EscapeHtml too. Also note that '() can still break CSS URLs. This function is charset agnostic and will not canonicalize overlong encodings. It is assumed that a UTF-8 string will be supplied. See escapeurlpathsegment.c.
Mon, 29 Mar 2021 15:37:13 GMT. See formathttpdatetime.c.
"1.2.3.4:31337"
Date header, which is now, give or take a second. The returned value is a UNIX timestamp.
name is case-insensitive. The header value is returned as a canonical UTF-8 string, with leading and trailing whitespace trimmed, which was decoded from ISO-8859-1. The returned value might contain separators, C0, C1, and even NUL characters. It is the responsibility of the caller to impose restrictions on validity if they're desired, since each specific header has its own rules for serialization. In the event that the client suplies raw UTF-8 in the HTTP message headers, the original UTF-8 sequence can be losslessly restored by counter-intuitively recoding the returned string back to Latin1.
Content-Type) will always have their casing normalized to what the RFC uses. Non-standard headers might have whatever casing the user specifies. This function is suboptimally designed and therefore likely to change in the future. Please consider using GetHeader instead if possible.
kLogDebug > kLogVerbose > kLogInfo > kLogWarn > kLogError > kLogFatal.
GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE, and OPTIONS. Everything else is rejected by the transport layer, using either a 401 or 501 Not Implemented response.
name is handled in a case-sensitive manner. This function checks Request-URI parameters first. Then it checks application/x-www-form-urlencoded from the message body, if it exists, which is common for HTML forms sending POST requests. If a parameter is supplied matching name that has no value, e.g. foo in ?foo&bar=value, then the returned value will be nil, whereas for ?foo=&bar=value it would be "". To differentiate between no-equal and absent, use the HasParam function. The returned value is decoded from ISO-8859-1 (only in the case of Request-URI) and we assume that percent-encoded characters were supplied by the client as UTF-8 sequences, which are returned exactly as the client supplied them, and may therefore may contain overlong sequences, control codes, NUL characters, and even numbers which have been banned by the IETF. It is the responsibility of the caller to impose further restrictions on validity, if they're desired.
application/x-www-form-urlencoded message body in the order they were received. This may contain duplicates. The inner array will have either one or two items, depending on whether or not the equals sign was used.
"/". It is further guaranteed that no "//" or "/." exists in the path. The returned value is returned as a UTF-8 string which was decoded from ISO-8859-1. We assume that percent-encoded characters were supplied by the client as UTF-8 sequences, which are returned exactly as the client supplied them, and may therefore may contain overlong sequences, control codes, NUL characters, and even numbers which have been banned by the IETF. redbean takes those things into consideration when performing path safety checks. It is the responsibility of the caller to impose further restrictions on validity, if they're desired.
"1.2.3.4:31337". If -p 0 was supplied as the listening port, then the port in this string will be whatever number the operating system assigned.
GetPath and GetParam.
9 for HTTP/0.9, 100 for HTTP/1.0, or 101 for HTTP/1.1.
application/x-www-form-urlencoded message body.
/ listing page to not display any paths beginning with prefix. This function should only be called from .init.lua.
-D flag was used. If slurping large file into memory is a concern, then consider using ServeAsset which can serve directly off disk.
GetLogLevel. If redbean is running in interactive mode, then this will log to the console. If redbean is running as a daemon or the -L LOGFILE flag is passed, then this will log to the file. Reasonable values for level are kLogDebug > kLogVerbose > kLogInfo > kLogWarn > kLogError > kLogFatal. The logger emits timestamps in the local timezone with microsecond precision. If log entries are emitted more frequently than once per second, then the log entry will display a delta timestamp, showing how much time has elapsed since the previous log entry. This behavior is useful for quickly measuring how long various portions of your code take to execute.
Mon, 29 Mar 2021 15:37:13 GMT to a UNIX timestamp. See parsehttpdatetime.c.
Server header, as well as the <h1> title on the / listing page. The brand string needs to be a UTF-8 value that's encodable as ISO-8859-1. If the brand is changed to something other than redbean, then the promotional links will be removed from the listing page too. This function should only be called from .init.lua.
Cache-Control and Expires header generation for static asset serving. A negative value will disable the headers. Zero means don't cache. Greater than zero asks public proxies and browsers to cache for a given number of seconds. This should only be called from .init.lua.
GetServerAddr or the -z flag to stdout.
301, 302, 307, or 308 then a redirect response will be sent to the client. This should only be called from .init.lua.
-D is used. This function is mutually exclusive with SetStatus and ServeError.
SetStatus and ServeAsset.
name is case-insensitive and restricted to non-space ASCII. value is a UTF-8 string that must be encodable as ISO-8859-1. Leading and trailing whitespace is trimmed automatically. Overlong characters are canonicalized. C0 and C1 control codes are forbidden, with the exception of tab. This function automatically calls SetStatus(200, "OK") if a status has not yet been set. The header buffer is independent of the payload buffer. Neither are written to the wire until the Lua Server Page has finished executing. This function disallows the setting of certain headers such as Date and Content-Range which are abstracted by the transport layer. In such cases, consider calling ServeAsset.
level are kLogDebug > kLogVerbose > kLogInfo > kLogWarn > kLogError > kLogFatal.
reason is optional since redbean can fill in the appropriate text for well-known magic numbers, e.g. 200, 404, etc. This method will reset the response and is therefore mutually exclusive with ServeAsset and ServeError. If a status setting function isn't called, then the default behavior is to send 200 OK.
You can have redbean run as a daemon by doing the following:
redbean.com -vv -d -L redbean.log -P redbean.pid kill -TERM $(cat redbean.pid) # 1x: graceful shutdown kill -TERM $(cat redbean.pid) # 2x: forceful shutdown
It's possible to modify global interpreter state later on in the
server's lifecycle. When running in daemon mode, using kill -HUP
$(pidof redbean.com) will instruct redbean to run the code
in .reload.lua from the main process,
will will be lazily propagated to client connections.
redbean will grow to whatever number of processes your system limits and
tcp stack configuration allow. Once functions like fork()
start to fail, redbean will enter meltdown mode where it begins
interrupting processes so that idle connections can close as quickly as
possible, while sending 503 Service Unavailable responses
from the main process until congestion subsides. This means that redbean
can be a good citizen in large systems where things like quotas and
intelligent load balancing apply.
redbean works best right now for use cases that involve a lot of small messages. For example, pipelining is supported which basically gives us HTTP/2-like performance using just HTTP/1.1. On the other hand, redbean currently doesn't have APIs for handling things like large file uploads. There's a 64kb limit on request message size, so that processes can stay tiny. redbean also won't service hidden files, directory traversalals, or unreasonably fragmented messages. Those few restrictions aside, redbean generally aims to follow Postel's maxim in the sense that it's liberal in what it accepts but conservative in what it sends.
redbean is designed to be an unsecure webserver. That means redbean is neither secure nor insecure. How much security you want to bolt on is entirely up to you. For example, HTTPS support can be trivially added by having TCP connections flow through a program like stunnel. redbean can also be compiled fully hardened with ASAN memory safety, since the Cosmopolitan C library has the only open source implementation of the Address Sanitizer runtime that's designed for production use.
# Note: Benchmarked on an Intel® Core™ i9-9900 CPU
$ wrk -H 'Accept-Encoding: gzip' -t 12 -c 120 \
http://127.0.0.1:8080/tool/net/redbean.html
Running 10s test @ http://127.0.0.1:8080/tool/net/redbean.html
12 threads and 120 connections
Thread Stats Avg Stdev Max +/- Stdev
Latency 18.27ms 131.81ms 1.71s 97.60%
Req/Sec 85.17k 10.73k 144.05k 82.75%
10221627 requests in 10.10s, 7.53GB read
Socket errors: connect 0, read 0, write 0, timeout 13
Requests/sec: 1012088.67
Transfer/sec: 763.48MB
Thanks for using redbean! If you like what you've seen and want to encourage more, then consider becoming a GitHub sponsor. PayPal donations are also accepted at jtunney@gmail.com.
redbean hacker news thread (1,998 upvotes)
αcτµαlly pδrταblε εxεcµταblε (671 upvotes)
justine's web page